Rectal Cancer Surgery: Types, Techniques, and What to Expect
Rectal cancer happens when abnormal cells develop in the rectum (the lower part of the large intestine). Rectal cancer is often grouped with colon cancer and is known as colorectal cancer. This is because both cancers develop in the large intestine and share the same characteristics.
According to the reports of the World Health Organisation, colorectal cancer is the third most common type of cancer, accounting for 10% of cancer cases. Moreover, it is also the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths.
Colorectal cancer often requires surgery as the key component of the treatment option. In many cases, rectal cancer surgery is the only curative option if the cancerous cells have not spread to other organs. Surgery is done to remove the original tumour. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is recommended to remove the metastatic lesions.
Now, rectal cancer surgery is of different types. In this blog, we will elaborate on this, explore the various techniques and discuss what you can expect before, after and during the procedure.
Types of Rectal Cancer Surgery
Before opting for surgery, your doctor will determine how close the tumour is to the anus. This helps to know the type of surgery required. Here are some of the common approaches:
- Polypectomy: It is a procedure where the polyps (small growths on the lining of the colon) are removed with the help of colonoscopy. The surgeon uses a special instrument called a colonoscope to look for the polyps and removes them before they turn cancerous.
- Local excision: It is a procedure that removes early-stage abnormal tissues, especially if the tumour is small and confined. Here, the surgeon pulls out the tumour along with some healthy surrounding tissues through the anus. This type is suggested for patients with rectal cancer in Stage 0 when the cancer has not spread and has a lower risk of recurrence.
- Transanal Excision (TAE): It is typically used to remove early-stage cancer, more specifically Stage 1, when the cancerous cells are small and confined to the walls of the rectal lining. Here, the surgeon cuts through the rectal wall to remove the cancer as well as some surrounding healthy tissues. The hole in the rectum wall is then closed.
- Low anterior resection: The surgeon suggests this type when the cancer is in the middle or upper rectum. The main goal of low anterior resection is to preserve the sphincter function. During this rectal cancer surgery, the surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen and removes the cancer along with the nearby normal tissues and the lymph nodes. The colon is then attached to the remaining rectum.
- Abdominoperineal Resection (APR): It is used to treat cancers that are low in the rectum and the anus, close to the sphincter muscles. In this type, the surgeon removes the rectum, the anus, and the surrounding healthy tissues, including the sphincter muscle. As the anus is removed, patients are required to have a permanent colostomy to allow the stools to pass.
- Total Mesorectal Excision (TME): It is a procedure where a significant length of the bowel around the tumour is removed. It is a common but complex procedure in the treatment of rectal cancer, involving the complete removal of the rectum along with surrounding fatty tissues, blood vessels and lymph nodes. The procedures ensure that both visible and microscopic cancer is eliminated, thereby reducing the risk of recurrence.
- Pelvic Exenteration: It is a more extensive procedure for rectal cancer. In this type of rectal cancer surgery, all organs within the pelvic cavity are removed, including the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum. It is used for treating advanced or recurrent cancers.
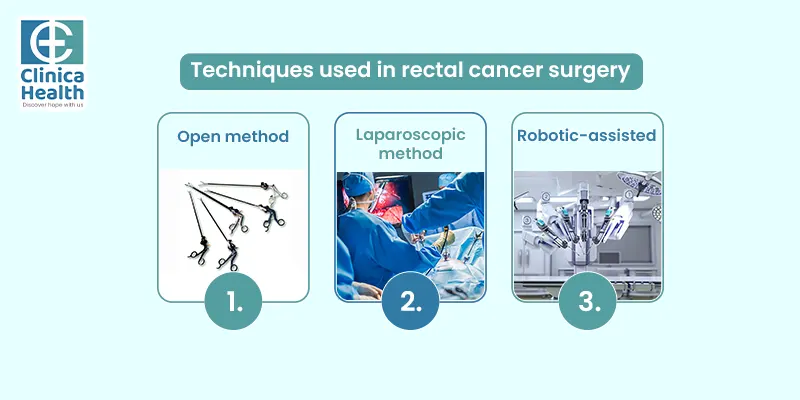
Techniques Used in Rectal Cancer Surgery
Here are the following approaches to rectal cancer surgery:
- Open method or laparotomy: It is a conventional procedure which involves making large incisions in the abdomen to access the rectum. While effective, the procedure requires a longer hospital stay, more post-operative pain and a slower recovery period. It is recommended for complex cases.
- Laparoscopic method: It is a minimally invasive procedure where fine tubes and blisters are inserted through three or 4 holes in the abdomen. Here, patients experience less blood loss, reduced pain, no scarring and quicker recovery.
- Robotic-assisted: It is a new and more advanced form of surgical intervention which allows for greater precision and flexibility. During the procedure, the surgeon operates a robotic surgical system that has a camera and mechanical arms with surgical instruments attached to them.
What to Expect Before Rectal Cancer Surgery?
Before rectal cancer surgery, patients are required to undergo various diagnostic procedures to check if they are eligible candidates for the operation, like blood tests and imaging scans, such as a colonoscopy and an MRI.
Individuals are also needed to follow pre-operative instructions to ensure that successful outcomes are achieved. This includes bowel cleansing, sticking to a liquid diet, quitting certain medications and discussing your concerns with the surgeon.
Life after Rectal Cancer Surgery
Recovery after rectal cancer surgery depends upon the procedure type and the individual’s health. Here are the following guidelines which patients are required to follow.
- Use pain relievers as instructed by the surgeon to manage pain and discomfort.
- Make sure to gently cleanse the wound. Ensure that it is dry and always covered to avoid infections.
- Minimise straining during bowel movements to prevent complications like the formation of piles and the opening of wounds.
- Avoid strenuous activities until complete recovery.
- Eat a balanced diet to meet your nutritional needs.
- Stay hydrated and take plenty of rest to promote healing.
- Take stool softeners to prevent constipation.
Conclusion
Rectal cancer surgery is a life-saving treatment that requires expert care. The goal of the different procedures is to remove the cancerous cells and increase the survival rate of patients. Understanding the surgical options and what to expect after the procedure will help fight the deadly disease with confidence.
 Call Now:
8010 552 552
7595 838 844
Call Now:
8010 552 552
7595 838 844
 Whatsapp Now:
8010 552 552
Whatsapp Now:
8010 552 552
 Email Me:
[email protected]
Email Me:
[email protected]

